工件/杂
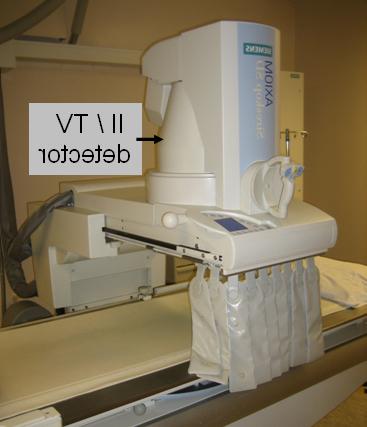
Two common artifacts in im年龄-intensified fluoroscopy and photospot imaging arise from the use of the im年龄 intensifier because of geometrical issues and internal light scatter. 第一个工件, 枕形失真, is caused by the spherical input phosphor structure and photocathode electron im年龄 mapped onto the planar output phosphor structure. Curvature of the input phosphor / photocathode causes a more severe distortion and greater distance between equidistant points 在外围 of the im年龄 compared to the center (similar to the way that pins placed in a pincushion are parallel in the center of the cushion but diverge 在外围). This distortion is more pronounced with the use of the large FOV, where the curvature of the input phosphor surface is the greatest at the edges of the im年龄. Typical 枕形失真 at the im年龄 periphery causes distortions on the order of +5% to +15%. Geometric distortion is less at the center of the im年龄.A corollary to 枕形失真 is known as S distortion, caused by the influence of external magnetic fields on the electron trajectories from the input phosphor to the output phosphor. This can result in a time-varying non-linear warping of the im年龄 as the II system is rotated; the distortion can be reduced by shielding the II with mu-metal magnetic field attenuators.
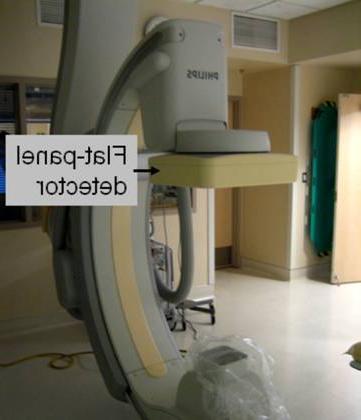
An im年龄 of a uniform phantom of small spherical attenuators placed with equal 1-cm spacing in the matrix is shown in 图一个. Note the geometric distortion 在外围 of the im年龄, with increased distance and non-linear mapping of the sphere locations. One advant年龄 of flat-panel detectors manufactured for fluoroscopy is the planar geometry of the scintillator, which eliminates the 枕形失真 artifacts as illustrated with the same phantom in 图B.
 |
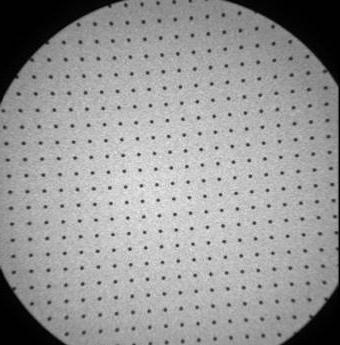 |
图一个. Left: Im年龄 intensifier-TV system for fluoroscopy applications. Right: Im年龄 of 枕形失真 of regularly-spaced phantom in the circularly collimated im年龄..
 |
 |
图B. Left: Flat-panel fluoroscopy/cineradiography system. Right: Im年龄 of regularly-spaced phantom, showing good geometric linearity of the rectangularly-shaped im年龄..
The second artifact/degradation is chiefly related to internal light scattering at the output phosphor, 这就是所谓的遮光, which results in a significant loss of im年龄 contrast particularly in im年龄 areas representing high x-ray attenuation in the object. Light from bright im年龄 areas spread into dark im年龄 areas, which significantly reduces im年龄 contrast. The contrast ratio is theS measurement of the im年龄 signal of a uniformly exposed II with no attenuators to the signal under a centered, highly attenuating lead disk of diameter equal to 10% of the input phosphor diameter. 在理想的情况下, the contrast ratio would be infinite under these conditions, but im年龄 intensifiers typically have values that range from 50 to 500, depending on many variables including output phosphor structure, optical coupling technology, 年龄, 等. Vignetting is another effect caused by light scatter within the active im年龄 area, and describes the increased intensity of a uniformly exposed im年龄 relative to the periphery. As light scatter is essentially isotropic (equal scatter in all directions) light scatter from the periphery contributes to the signal in the center, but there is no light scatter outside of the active im年龄 area contributing to the signal 在外围.
